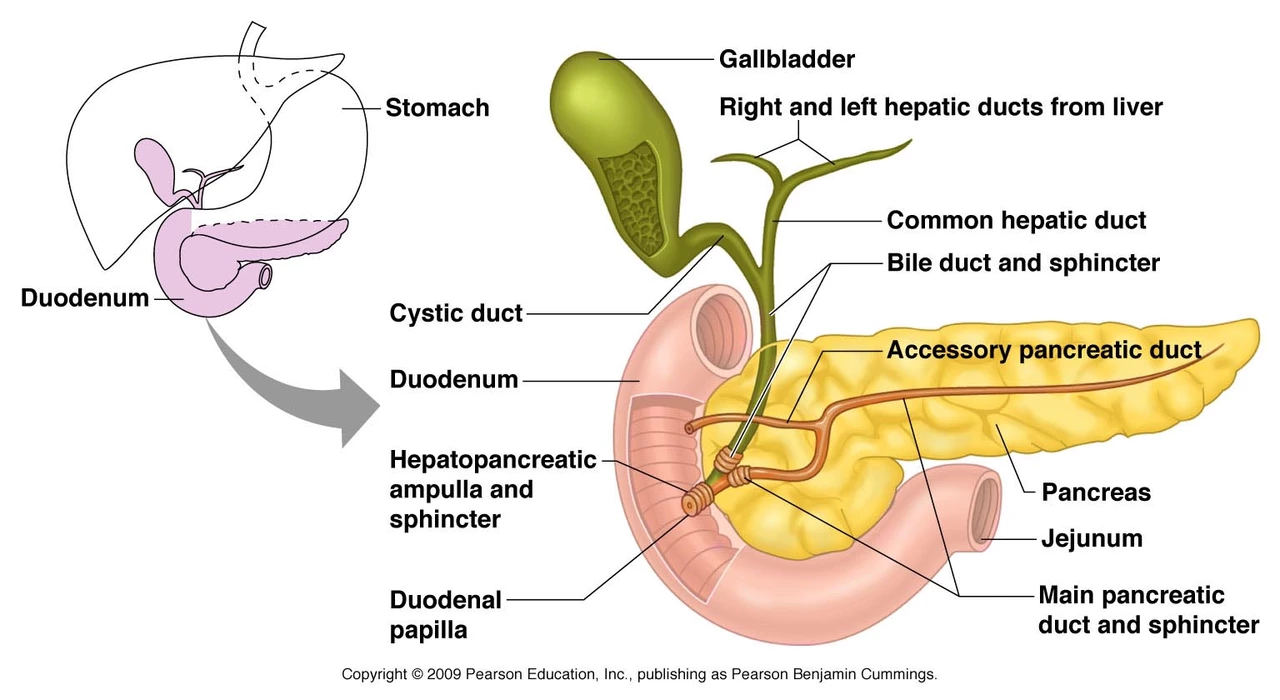
Understanding Pancreatic Duct Blockage
Pancreatic duct blockage, also known as pancreatic duct obstruction, is a serious health condition that affects the pancreas. The pancreas is an important organ in our digestive system, responsible for producing digestive enzymes and hormones like insulin. When the pancreatic duct becomes blocked, it can lead to several complications, such as pancreatitis and even pancreatic cancer. In this section, we will delve into the causes and symptoms of pancreatic duct blockage, as well as the importance of early detection and diagnosis.
Causes and Risk Factors for Pancreatic Duct Blockage
There are several factors that can contribute to pancreatic duct blockage. Some of the most common causes include gallstones, chronic pancreatitis, and pancreatic tumors. Other factors, such as abdominal trauma, autoimmune pancreatitis, and genetic predisposition, can also increase the risk of developing a blockage. Understanding these risk factors and addressing them early on can significantly reduce the chances of experiencing pancreatic duct blockage and the complications it brings.
How to Diagnose Pancreatic Duct Blockage
Diagnosing pancreatic duct blockage is essential for timely and effective treatment. Some of the diagnostic tools used by healthcare professionals include imaging studies like computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). Blood tests and pancreatic function tests can also help in confirming the diagnosis. It is important to consult with your healthcare provider if you experience any signs or symptoms suggestive of pancreatic duct blockage, such as abdominal pain, jaundice, or unexplained weight loss.
Treatment Options for Pancreatic Duct Blockage
Treatment for pancreatic duct blockage depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some of the most common treatment options include endoscopic procedures, such as ERCP, to remove the blockage or stent placement to keep the duct open. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the obstruction or even the affected part of the pancreas. Pain management and supportive care, such as dietary modifications and enzyme replacement therapy, can also help in managing the symptoms and improving the quality of life for patients with pancreatic duct blockage.
The Role of Patient Education in Managing Pancreatic Duct Blockage
Patient education plays a crucial role in managing pancreatic duct blockage. By providing patients with accurate information about their condition, healthcare professionals can empower them to take an active role in their treatment and recovery. This includes understanding the importance of adhering to prescribed medications and treatments, making necessary lifestyle changes, and promptly reporting any new or worsening symptoms to their healthcare provider. Educated patients are more likely to be proactive in their care, which can ultimately lead to better health outcomes.
Nutrition and Pancreatic Duct Blockage
Proper nutrition is essential in managing pancreatic duct blockage, as it helps to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. A dietitian or nutritionist can provide guidance on the best dietary practices for patients with this condition, which may include consuming smaller, more frequent meals, avoiding high-fat foods, and incorporating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into the diet. Additionally, enzyme replacement therapy can help patients with pancreatic duct blockage properly digest and absorb nutrients from their food, further supporting their overall health and well-being.
Lifestyle Changes for Pancreatic Duct Blockage Management
Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve the quality of life for patients with pancreatic duct blockage. Some of these changes include quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and engaging in regular physical activity. These lifestyle modifications can not only help in managing symptoms but also reduce the risk of developing complications and improve overall health.
Emotional and Mental Health Support
Dealing with pancreatic duct blockage can be emotionally and mentally challenging for patients and their families. It is essential to address these challenges and provide support to help patients cope with their condition. This can include individual counseling, support groups, or even online forums where patients can connect with others who are going through similar experiences. Emotional and mental health support can greatly improve a patient's quality of life and overall well-being.
Importance of Regular Follow-Up
Regular follow-up visits with healthcare providers are essential for patients with pancreatic duct blockage. These visits allow healthcare providers to monitor the patient's condition, adjust treatment plans as needed, and address any new or worsening symptoms. Following a consistent follow-up schedule can help ensure the best possible outcomes for patients with pancreatic duct blockage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, patient education is vital in managing pancreatic duct blockage. By understanding their condition, patients can take an active role in their treatment and make informed decisions about their care. Proper nutrition, lifestyle changes, emotional support, and regular follow-up visits are all essential components of a comprehensive management plan for pancreatic duct blockage. By working closely with their healthcare team, patients can effectively manage their condition and enjoy a better quality of life.


John Babko
May 6, 2023 AT 05:03Education is the powerhouse that drives patients to take charge of pancreatic duct blockage!!; By understanding the anatomy, the risks, and the treatment options, patients can steer their health journey with confidence!!!; No more passive waiting-active learning saves lives; knowledge translates into timely appointments, adherence to enzyme therapy, and smarter lifestyle tweaks!!!
Stacy McAlpine
May 11, 2023 AT 05:03Knowing what’s happening inside the pancreas helps you make smart choices-eat smaller meals, avoid greasy foods, and stick to your doctor’s plan. It’s not just about pills; it’s about lifestyle, too.
Roger Perez
May 16, 2023 AT 05:03🤔 When we view the pancreas as a tiny orchestra, education becomes the conductor-guiding each instrument to play in harmony. 🎶 Empowered patients can transform chaos into a steady rhythm of health, one bite at a time.
michael santoso
May 21, 2023 AT 05:03The discourse surrounding patient education in pancreatic duct obstruction is often marred by a puerile simplification that betrays the intellectual rigor our discipline demands. One must first acknowledge that the pathophysiology of ductal obstruction is a nexus of biliary calculus formation, neoplastic encroachment, and inflammatory fibrosis, each demanding a nuanced pedagogical approach. A cursory pamphlet replete with layman analogies fails to convey the gravitas of enzymatic insufficiency and its systemic sequelae. Moreover, the prevailing didactic models neglect the epistemological underpinnings of self-efficacy theory, thereby rendering education a perfunctory ritual rather than a transformative praxis. In my estimation, a stratified curriculum-segmenting basic anatomical awareness from advanced endoscopic decision‑making-would better serve the erudite patient. Such a curriculum must be buttressed by peer‑reviewed literature, not the anecdotal lore that proliferates in generic clinic handouts. The integration of high‑resolution MRCP imaging into teaching modules exemplifies the synthesis of visual cognition with biochemical insight. Equally, the omission of psychosocial determinants in most educational schemas reveals a myopic focus on physiological metrics. Patients, when apprised of the intricate interplay between stress, smoking cessation, and ductal patency, are more inclined to adopt holistic interventions. It is incumbent upon clinicians to eschew the paternalistic monologue and instead foster a dialogic exchange predicated on mutual respect. The elevation of patient agency, through explicit instruction on stent maintenance and enzyme dosing schedules, mitigates the risk of iatrogenic complications. Furthermore, the deployment of longitudinal follow‑up dashboards, accessible via patient portals, sustains engagement beyond the initial consultation. A failure to incorporate such sophisticated tools relegates the educational endeavor to a mere formality, eroding trust. In sum, the sanctity of patient education in this realm demands an intellectual standard commensurate with the complexity of the disease itself; anything less is an affront to both science and the patient’s dignity. Only through such rigorous pedagogy can we hope to curtail the morbidity associated with pancreatic duct blockage.
M2lifestyle Prem nagar
May 26, 2023 AT 05:03Stay informed, stay strong.
Karen Ballard
May 31, 2023 AT 05:03Remember to use the Oxford comma when listing symptoms, medications, and lifestyle changes 😊
Gina Lola
June 5, 2023 AT 05:03From an endoscopic standpoint, ERCP with sphincterotomy remains the gold standard for ductal decompression, yet adjunctive stenting can mitigate post‑procedural strictures.
Leah Hawthorne
June 10, 2023 AT 05:03It’s great that you’re looking into diet tweaks; incorporating low‑fat meals can really ease enzyme demand.
Brian Mavigliano
June 15, 2023 AT 05:03While everyone praises patient education as the panacea, one could argue that without systemic healthcare reform, knowledge alone is but a paper lantern in a storm.
Emily Torbert
June 20, 2023 AT 05:03Feeling overwhelmed is normal its okay to take it one step at a time and lean on your support network
Rashi Shetty
June 25, 2023 AT 05:03It is incumbent upon healthcare providers to furnish patients with comprehensive, evidence‑based information regarding pancreatic duct obstruction. Such information should encompass etiological factors, diagnostic modalities, and therapeutic options, thereby facilitating informed consent. Moreover, the discourse must be delivered in a culturally sensitive manner, respecting linguistic nuances and health literacy levels. Failure to do so not only jeopardizes patient autonomy but also engenders suboptimal adherence. 📚
Queen Flipcharts
June 30, 2023 AT 05:03In the grand tapestry of medical stewardship, the patient’s intellect serves as the crucible wherein national resilience is forged; thus, the dissemination of precise knowledge about pancreatic duct pathology is a patriotic duty.
Yojana Geete
July 5, 2023 AT 05:03Oh dear the drama of a blocked duct unfolds like a tragic play the hero must heed the counsel of the wise yet the world turns a blind eye
Jason Peart
July 10, 2023 AT 05:03Hey there! Remember you’re not alone in this-talk to a dietitian, join a support group, and dont be afraid to ask your doc any question. We’ll get throuh this together!
Hanna Sundqvist
July 15, 2023 AT 05:03Some say the meds are fine but I read that big pharma hides side effects of enzyme therapy
Jim Butler
July 20, 2023 AT 05:03Let us rally together, dear patients, and embrace the regimen with unwavering vigor; your perseverance shall be rewarded 🏅
Ian McKay
July 25, 2023 AT 05:03The patient’s education material should be revised; it contains several misplaced modifiers and inconsistent tense usage.
Deborah Messick
July 30, 2023 AT 05:03Contrary to popular belief, emphasizing nutrition above procedural intervention may inadvertently delay necessary surgical management.