Weight Loss Option Finder
Find Your Best Weight Loss Option
Answer a few quick questions to identify the most appropriate weight loss option for you based on your unique circumstances.
Key Takeaways
- Orlijohn is a brand of orlistat that blocks fat absorption and requires a low‑fat diet.
- Prescription‑strength alternatives (Xenical) and over‑the‑counter options (Alli) have similar mechanisms but differ in dosage and cost.
- Other FDA‑approved weight‑loss medicines-phentermine, liraglutide, semaglutide-work through appetite suppression or hormone regulation, not fat blockage.
- Choosing the right option depends on your health profile, budget, and willingness to manage side effects.
- Non‑drug approaches like medically supervised low‑calorie diets or bariatric surgery can be more effective for high BMI patients.
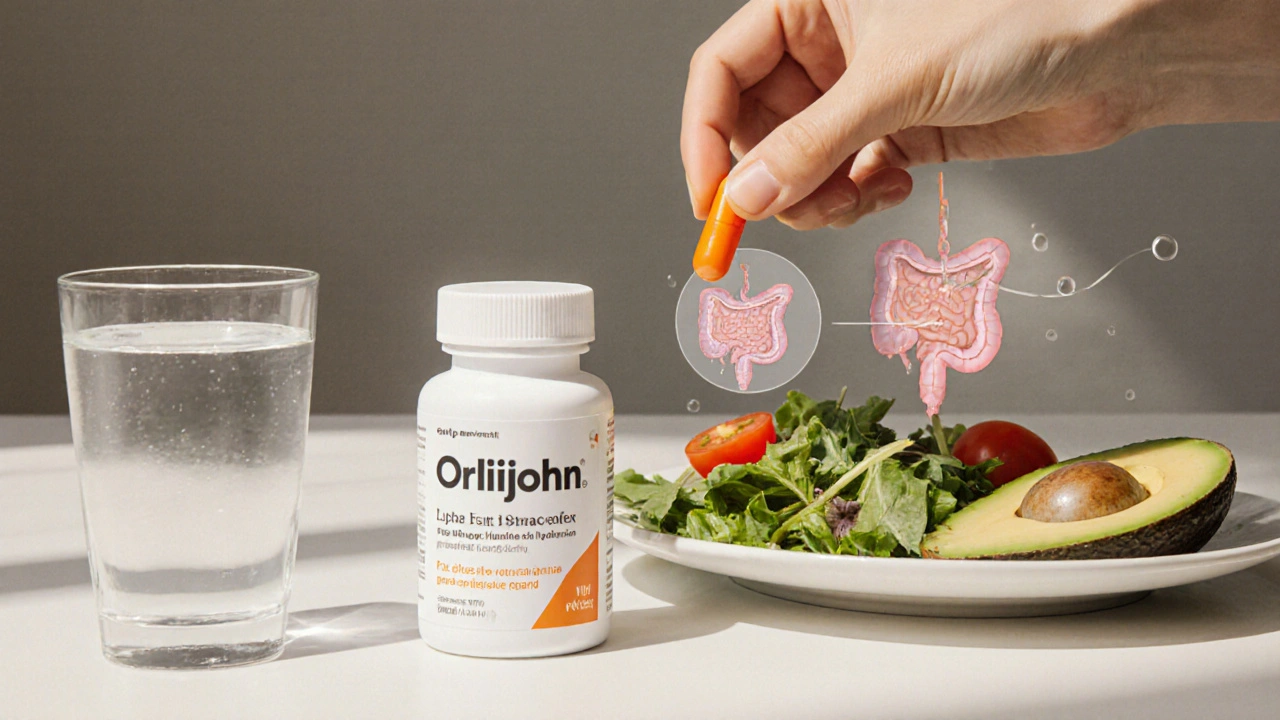
What Is Orlijohn?
Orlijohn is marketed as a generic version of the weight‑loss drug orlistat, sold in 120mg capsules and usually required by prescription in many countries. It works by inhibiting lipase enzymes in the gut, so about 30% of dietary fat passes through without being absorbed.
Because the drug does not affect appetite, users must pair it with a reduced‑fat diet to avoid oily stools, gas, and urgency-common side effects that signal the medication is doing its job.
How Orlistat Works (and Why It Matters)
Orlistat’s active ingredient binds to the active site of pancreatic lipase. When the enzyme can’t break down triglycerides, the undigested fat is excreted. This mechanism is unique among FDA‑approved anti‑obesity agents, which typically target hunger signals.
Key implications:
- Weight loss is modest-averaging 3-5% of baseline body weight after one year.
- Effectiveness is tightly linked to dietary fat intake; high‑fat meals dilute the drug’s impact.
- Because the drug works locally in the gut, it has minimal systemic absorption, reducing risk of cardiovascular side effects.
Main Alternatives to Orlijohn
Below are the most common alternatives, each with its own pros, cons, and cost profile.
Xenical (Prescription Orlistat)
Xenical is the brand‑name version of orlistat, available in 120mg capsules. It’s essentially the same molecule as Orlijohn but costs more because of branding and tighter regulation.
Alli (OTC Orlistat)
Alli contains a lower 60mg dose of orlistat and can be bought over the counter in many countries. It’s marketed for people with a BMI≥25 who want a modest weight‑loss boost.
Phentermine
Phentermine is a stimulant that suppresses appetite by releasing norepinephrine in the brain. It’s usually prescribed for short‑term use (up to 12 weeks) and can lead to a 5-10% body‑weight reduction.
Liraglutide (Saxenda)
Liraglutide is a GLP‑1 receptor agonist originally approved for type‑2 diabetes (as Victoza) but at a higher dose it’s marketed for weight loss. It works by slowing gastric emptying and enhancing satiety.
Semaglutide (Wegovy)
Semaglutide, another GLP‑1 agonist, is given as a weekly injection and has shown 15% average weight loss in clinical trials-among the highest for any medication.
Bariatric Surgery
Procedures like gastric sleeve or Roux‑en‑Y bypass physically restrict food intake or nutrient absorption. They’re invasive, expensive, but can lead to 30‑%+ weight loss.
Low‑Calorie Diet Programs
Clinically supervised programs (e.g., medically‑supervised Very Low‑Calorie Diets) rely purely on diet, often delivering rapid weight loss without medication.
Side‑by‑Side Comparison
| Brand / Generic | Mechanism | Prescription? | Typical Cost (USD / month) | Average Weight Loss (12mo) | Main Side Effects | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orlijohn (Orlistat) | Fat‑absorption blocker | Yes | $30-$45 | 3-5% | Oily stools, flatulence, fat‑soluble vitamin deficiency | People who can stick to low‑fat diet |
| Xenical (Orlistat) | Fat‑absorption blocker | Yes | $70-$100 | 3-5% | Same as Orlijohn | Those who prefer brand name & can afford it |
| Alli (Orlistat 60mg) | Fat‑absorption blocker (half dose) | No | $30-$40 (OTC) | 2-3% | Milder GI symptoms | First‑time users, lower BMI |
| Phentermine | Appetite suppressant (stimulant) | Yes | $20-$35 | 5-10% | Increased heart rate, insomnia, dry mouth | Short‑term jump‑start, no heart issues |
| Liraglutide (Saxenda) | GLP‑1 agonist - slows gastric emptying | Yes | $1100-$1300 | 8-10% | Nausea, vomiting, pancreatitis risk | Patients with pre‑diabetes or diabetes |
| Semaglutide (Wegovy) | GLP‑1 agonist - strong satiety signal | Yes | $1300-$1500 | 12-15% | Nausea, gallbladder disease, injection site reactions | Those seeking the biggest loss and can afford weekly injection |
| Bariatric Surgery | Mechanical restriction / malabsorption | No (procedure) | $15,000-$30,000 (one‑time) | 30-35% | Operative risks, lifelong dietary changes | Severe obesity (BMI≥40) or BMI≥35 with comorbs |
How to Pick the Right Option for You
Use the following checklist to narrow down the best fit:
- Medical History: If you have a history of gallstones, pancreatitis, or chronic diarrhea, avoid orlistat‑based products.
- Budget: OTC Allies are cheap, but GLP‑1 agonists can cost >$1,200/month.
- Weight‑Loss Goal: Want a 3‑5% drop? Orlistat styles work. Aim for 15%+? Look at semaglutide or surgery.
- Lifestyle Commitment: Orlistat needs a low‑fat diet; GLP‑1 drugs require daily or weekly injections.
- Time Horizon: Phentermine is short‑term; bariatric surgery is permanent.
Talking to a healthcare provider is essential. They can run baseline labs (lipid panel, liver enzymes, blood glucose) and decide whether a lipase inhibitor or an appetite‑suppressant aligns with your physiology.
Managing Side Effects & Maximizing Results
If you choose Orlijohn or any orlistat product, keep these tips in mind:
- Take the capsule **with a meal** that contains no more than 30% fat. If the meal is fat‑free, skip the pill.
- Supplement with a multivitamin that includes vitamins A, D, E, and K-these are the fat‑soluble ones your body might miss.
- Stay hydrated. GI discomfort often worsens when you’re dehydrated.
- Log your meals. Seeing fat percentages on paper (or an app) helps you stay within the safe range.
For GLP‑1 drugs, start with a low dose and titrate up to reduce nausea. For phentermine, avoid caffeine and alcohol to keep heart rate steady.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I take Orlijohn and Alli together?
No. Both contain the same active ingredient (orlistat). Using them together would double the dose, increasing GI side effects without added benefit.
How long does it take to see results with Orlijohn?
Most users notice a modest weight drop (0.5-1kg) after 4-6 weeks if they stick to a low‑fat diet. Full 12‑month results average 3-5% of initial weight.
Is semaglutide safe for people without diabetes?
Yes. Wegovy is FDA‑approved for obesity in adults with a BMI≥30 (or≥27 with weight‑related conditions). Clinical trials showed no major safety concerns beyond the usual nausea and injection‑site reactions.
Do I need to keep taking Orlijohn forever?
Orlistat is meant for long‑term weight‑maintenance. If you achieve your goal and maintain a healthy diet, many doctors suggest tapering off after 12-18 months, but a gradual reduction is safer than stopping abruptly.
What’s the biggest drawback of bariatric surgery compared to pills?
The invasiveness. Surgery carries anesthesia risks, requires a hospital stay, and demands lifelong dietary monitoring. Pills are non‑invasive but usually deliver smaller weight loss.
Bottom line: there’s no one‑size‑fits‑all answer. Orlijohn vs alternatives comes down to how aggressive you want to be, what you can afford, and whether your body tolerates a fat‑blocking drug. Use the checklist, talk to a clinician, and pick the tool that fits your life-then stick with it for the best chance at lasting results.



Val Vaden
October 14, 2025 AT 02:00Orlistat works, but you’ll be dealing with greasy stools – worth it 🤷♂️
lalitha vadlamani
October 15, 2025 AT 07:10While the allure of rapid weight loss is tempting, it is imperative that individuals prioritize holistic health over fleeting aesthetic gains; adherence to evidence‑based interventions, coupled with diligent medical supervision, remains the cornerstone of sustainable well‑being.
kirk lapan
October 16, 2025 AT 12:03I have been reading up on Orlijohn and all its rivals for years, and let me tell you the science is far more nuanced than the hype suggests.
First, orlistat’s mechanism of blocking fat absorption is literally a gut‑level trick that doesn’t mess with your brain chemistry like those GLP‑1 drugs.
That means you won’t get the euphoric hunger suppression, but you also sidestep the jittery side effects.
However, the trade‑off is a literal oily after‑effect that many newbies find downright disgusting.
If you don’t cut your dietary fat to roughly thirty percent, the pills just sit there and let the fat pass, resulting in those notorious oily stools.
I’ve seen patients who ignore the diet and end up with vitamin deficiencies, especially A, D, E, and K, because the fat‑soluble vitamins are excreted with the fat.
Supplementing with a good multivitamin is non‑negotiable, yet the market is flooded with cheap copies that barely cover the basics.
Budget‑wise, Orlijohn sits comfortably between the expensive Wegovy injections and the cheap OTC Alli, but you still need to budget for the vitamins and possibly a dietitian.
From a compliance standpoint, taking a pill with every meal feels burdensome for some, especially when you’re dining out and can’t precisely measure fat content.
Contrast that with semaglutide, where a weekly injection can be forgotten after a coffee, and you get up to fifteen percent weight loss on average.
Phentermine, on the other hand, is a stimulant; it can raise blood pressure and should be avoided if you have any cardiac issues.
The real winner, in my opinion, is not the drug but the structured lifestyle program that accompanies any pharmacologic choice.
When you pair low‑fat meals, regular exercise, and monitoring labs, even Orlijohn can push you past the three‑to‑five percent plateau that many deem insufficient.
Don’t forget that long‑term maintenance often requires you to taper off the medication after a year or so, lest you become dependent on the pill for any weight stability.
In summary, pick the tool that matches your health profile, budget, and willingness to endure the inevitable gastrointestinal side effects, and never forget that no pill replaces disciplined nutrition.
Landmark Apostolic Church
October 17, 2025 AT 16:56Weight loss is not merely a numbers game; it’s a cultural narrative about self‑control, and when you chase a pill you’re essentially buying into a shortcut that the industry sells to keep us all chasing the next “miracle”.
Matthew Moss
October 18, 2025 AT 22:06From an American perspective, we should demand affordable solutions, and Orlijohn offers a domestic alternative that doesn’t require importing exorbitant GLP‑1 drugs.
Antonio Estrada
October 20, 2025 AT 03:16I appreciate that perspective; however, we must also consider the individual’s metabolic profile and ensure that any chosen therapy aligns with their specific health metrics.
Andy Jones
October 21, 2025 AT 08:26Sure, because nothing says “I’m committed to health” like popping a fat‑blocking capsule and hoping your diet magically improves.
Kevin Huckaby
October 22, 2025 AT 13:36Yo, if you don’t want to be that oily‑sauce person at the buffet 🍽️, just pick a low‑fat plate and let Orlijohn do its thing – 🎯💪.
Brandon McInnis
October 23, 2025 AT 18:46Let’s not forget the human side of this journey; the frustration of battling cravings can feel like a storm, yet every small victory, like a week without oily fallout, is a triumph worth celebrating.
Todd Peeples
October 24, 2025 AT 23:40In clinical practice, the pharmacokinetic profile of orlistat demonstrates a localized gastrointestinal action, yielding a marginally superior safety margin relative to systemic appetite suppressants, albeit at the expense of modest efficacy metrics.
Chris Smith
October 26, 2025 AT 03:50Wow another miracle pill nobody wants to admit works only if you actually eat right.
Leonard Greenhall
October 27, 2025 AT 09:00The data indeed supports that adherence to a low‑fat regimen is the primary determinant of orlistat’s efficacy, as demonstrated by multiple randomized controlled trials.
Abigail Brown
October 28, 2025 AT 14:10Keep your head up – every disciplined meal is a step toward the larger goal, and the right medication can just amplify the progress you’re already making.
Crystal Slininger
October 29, 2025 AT 19:20Don’t be fooled; the big pharma lobby pushes semaglutide to keep us dependent on injections while they hide the cheap, effective alternatives like Orlijohn from mainstream awareness.